FDA Regulations Effecting Blood Centers
Like all Biomedical items, Blood donations are a highly regulated substance. The FDA and their subdivision, the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) collaborate to make sure hospitals and blood centers are keeping their establishments and operations suitable for a safe donation and transfusion. Both institutions do their best to ensure patients are getting their treatment as safely as possible. Noncompliant blood centers are harshly dealt with by the FDA and can result in fines reaching in the millions (Forbes). Understanding how the FDA implements their standards will help blood centers avoid fines and adopt proper solutions.
The FDA works to regulate blood donations and transfusions. CBER is an organization within the FDA that closely monitors healthcare centers, routinely inspecting an establishment’s status. Investigations take place every two years, searching for deviant procedures and unsuitable environments. During these inspections, CBER focuses on a few key areas. Blood centers are scanned for accurate record procedures and safe operations, along with testing for hazardous agents. The CBER is wary of the dangers associated with blood products and expects establishments to uphold their quality mandates. As stated by fda.gov, “problem” centers are inspected at an even higher rate. Chances are, if noncompliant centers are in operation, they will eventually be exposed.
Blood items require accurate data and traceability to pass inspections. The FDA has strengthened their standards in recent years, demanding an accurate record keeping system to keep track of unsuitable donors, movement of biologic items, and successful transfusions. The FDA views accurate records and traceability as an effective way to reduce transfusion errors and maximize patient safety. According to the FDA, budgeting issues are NOT an excuse for noncompliance. With the right integrator, there is a way to reach compliance without breaking the bank. Barcode scanning is a common, cost-effective solution for tracking. Alternatives like RFID tagging technology have also been used in the past with successful results.
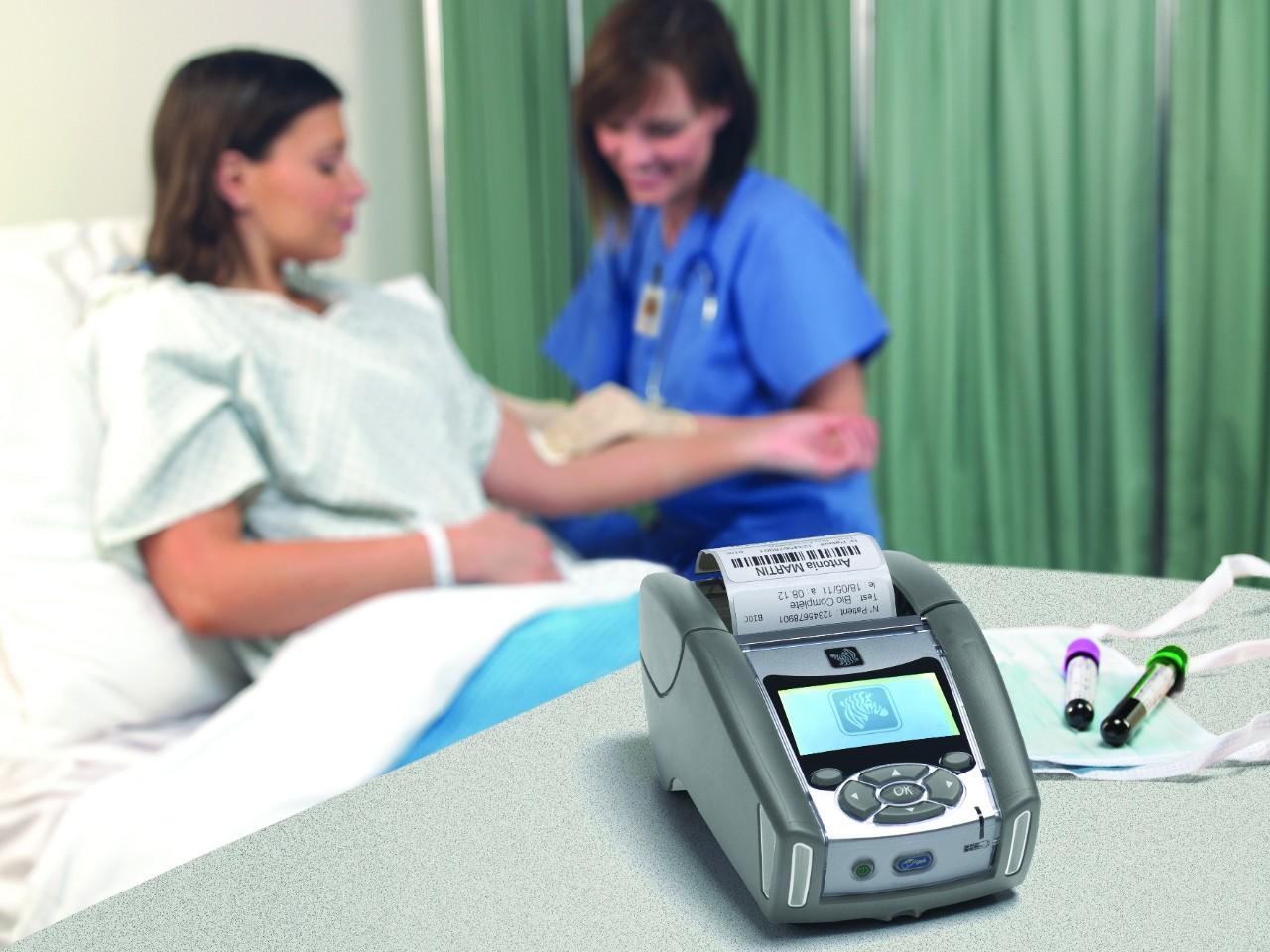
Without FDA regulations, millions of patients would be at risk. According to Blood Centers of the Pacific, someone needs blood every two seconds. To top it off, only 37% of the population is considered eligible to donate. With such a small percentage of eligible donors, every donation counts. The FDA acknowledges how critical an accurate transfusion is to a person’s life and will take necessary actions to minimize error. Fines have reached millions in the past to deter future offenders. A few common causes for fining have been under-staffing, inadequate training, and poor record systems (Forbes). The FDA’s job is to reduce the occurrence of these issues and improve the process as a whole.
Over the years, Symbology Enterprises have become experts in developing cost-effective, accurate blood center record keeping systems. We understand common operational problems and budgeting issues blood centers face. Using our knowledge of printing, scanning, and data integration, we have developed simple solutions like the Barcode Duplicator. Barcode duplication eliminates human error from the donation to transfusion workflow. Mistakes can impact a patient’s life forever. The FDA has set the framework for exceptional care… Now it is just a matter of reaching out for help. For more information on FDA policies please click on the articles of reference and fill out the form below!
Articles for reference:
http://www.fda.gov/BiologicsBloodVaccines/BloodBloodProducts/
http://www.bloodcenters.org/blood-donation/facts-about-blood-donation/

